Our environment and landscape are continuously evolving due to changing societal needs, the development of new construction methods, improved technology, and building practices which directly impact our buildings’ appearance, functionality and longevity. Consequent building sturdiness is especially noticeable in countries prone to tornados and earthquakes since improved technological designs allow buildings to be more flexible (bendable to a degree) in the face of these natural occurrences. It can be said that both architects and engineers play a pivotal role in shaping our environments, seamlessly blending functionality with aesthetics. Their expertise not only defines the skyline of our cities and the innovative design of our living and working spaces but also constantly enhances our daily lives. Architecture is a very wide and specialised sphere which is constantly facing – and resolving – new challenges with cutting-edge design solutions. This article briefly covers the role of architects and their impact on our external environment.

What Does an Architect Do?
Architects are not simply builders; they are skilled visionaries who transform original ideas into reality. An architect primarily focuses on the design, planning, and overseeing of construction projects. They are also involved in the transformation of older or historic structures into modern, functional spaces, preserving history whilst also meeting current needs.
As such, their responsibilities include:
- Innovative and visionary design: The initial work begins when architects meet with their clients to gain an understanding of the client’s general vision and purpose, providing advice through brainstorming with the client or the architectural team, and drawing up initial sketches for illustrative purposes. This gives the proposed project a physical format on which to build the final concept.
- Environmental and community planning: On more expansive projects, such as factories, and commercial and housing developments particularly, experienced and knowledgeable architects take into consideration issues such as the existing conditions and best use of the planned site. Environmental aspects are also considered, as well as the wider impact of the development on the surrounding community. This ensures that developments are sustainable, functional and practical, and integrate seamlessly into their surrounding community. As environmental concerns broaden, architects are placing a greater emphasis on sustainable design practices. Sustainable architecture aims to minimise the carbon footprint of buildings through the use of eco-friendly materials and renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines, using recycled or locally sourced materials which reduce the impact on the environment and help to promote local economies. In addition, the well-being of the building’s occupants is safeguarded through the selection of materials that do not contain or emit harmful chemicals. This approach not only supports environmental health but can also provide clients with valuable savings through improved energy efficiency.
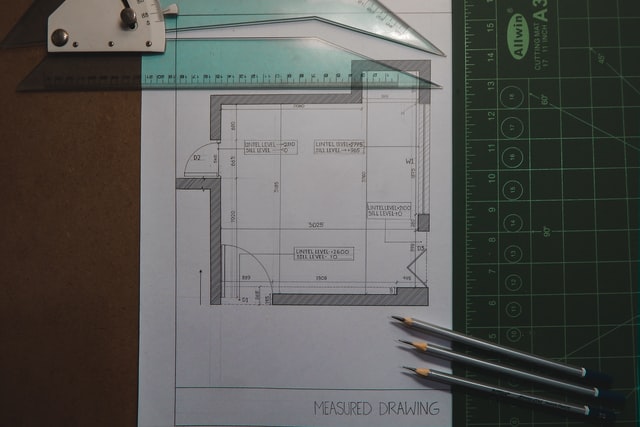
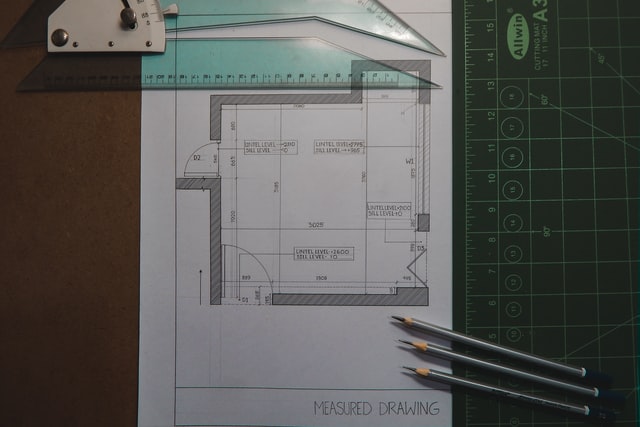
- The creation of technical drawings and specifications in the form of detailed blueprints or architectural drawings – sketch plans, diagrams or schematics – that convey detailed information about a building. Architects and designers create these types of technical drawings during the planning stages of a construction project, and in this way, they cover everything related to the building work. This will include the materials to be used, the safeguards to be incorporated into the construction (engineering aspects), and the layout and appearance of the building project. These blueprints, also referred to as construction drawings, construction plans, building plans, house plans, floor plans, and working drawings, show the internal and external layout of the building. Blueprints include:
- site plans, illustrating the building’s or project’s orientation on the land, including property lines, landscape features, driveways and utility lines
- floor plans, representing an aerial view of the building, clearly indicating the layout of walls, windows and doors and in-built furniture features such as fireplaces, cupboards, etc.
- a ceiling plan, also known as a reflected ceiling plan (RCP), is a drawing that shows the layout of a room’s ceiling in terms of the location of ceiling-mounted objects such as lights, vents, skylights, sprinklers and fans. This plan enables architects, engineers, and builders to understand how the ceiling is constructed and how the various elements relate to each other as it assists in the coordination of the building process by ensuring that factors such as the heating, ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) ductwork or overhead sprinkler systems do not interfere with the proposed lighting layout
- elevations and section drawings, which show the vertical layout of the building or project, illustrating its appearance from different sides. This gives an overview of the complete design from every viewpoint.
Blueprints are also important as they provide a detailed record of the intricacies of the building’s design and materials, which is important for future maintenance. Blueprints are used by builders to ensure that the design is accurately followed.
Architects are often involved in the project management aspects of the building process, to maintain quality standards and to ensure that the original design is adhered to throughout the build. They will liaise with the contractors, builders, engineers and other professionals, for example, landscape designers, plumbers, electricians, and roofing specialists, among others, to finalise the final project.
A Final Word on the Future of Architecture
As previously stated, the field of architecture is constantly evolving. Trends becoming more prevalent are the development of Smart Buildings, in which technology is integrated for improved energy management, security, and communication, Biophilic Design, which focuses on creating environments that foster a connection between people and nature, enhancing well-being through the use of natural light, greenery, and organic materials, and the development of Modular Construction, in which prefabricated components are made available to offer flexibility and productivity, saving time on construction processes and cutting down on unnecessary waste.
In Summary:
Architecture is yet another profession that is not immune to the constant demand for new technological innovations and adaptations to meet a constantly changing society and landscape. Architects seamlessly merge functionality and beauty, constantly pushing the boundaries of design possibilities. The need for stronger, yet more flexible, structures has cemented the bond between architects, engineers, environmental specialists and other skilled professionals who can add to the knowledge pool involved in construction and building projects across all sectors of society. Architects are the engine of the knowledge and skills train in this respect and their unique approach, adaptability and need for sustainability and environmental health will continue to move their profession forward in meeting new challenges as and when they present themselves.